Can advanced liver cancer be treated? Many people believe that cancer is an incurable disease. Especially when it comes to a person suffering from liver cancer, he must be said to be incurable because he is terminally ill. For the patients themselves, they often become pessimistic and desperate because they know it is liver cancer, especially in the late stage. Thereupon, they give up treatment, just waiting for death to come.
Treatment as Early as Possible can Prolong Survival
As a malignant tumor, liver cancer has a great chance of being cured or survival can be prolonged if it is discovered early and treated in time. According to the stage and 5-year survival rate of liver cancer, the 5-year survival rate of early primary liver cancer is 31%. The 5-year survival rate of locally invasive and lymph node metastatic liver cancer is 11% and distal metastatic liver cancer is 3% (data from Internet). The earlier liver cancer is treated, the more likely it is to be cured.
Treatments for Liver Cancer
Surgical resection: big trauma and high risk
Chemotherapy and electrotherapy: They are often accompanied by side effects, such as alopecia, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, etc. The overall outcome of chemotherapy is unsatisfying. Only about 7% of the patients can be relieved, and another 15% can achieve a longer expected survival time than those who did not receive chemotherapy. Moreover, this prolongation does not mean the cancer could be cured. Does not even mean the restoration of quality of life [1]
“CCC+P” treatment mode could effectively increase survival rate and improve life quality
“CCC+P” treatment mode is the achievement presented by Guangzhou Fuda Cancer hospital Research Institute and Guangzhou Cancer Cryoablation Research Institute. It combines the advantages and functions of the main clinical diagnosis and treatment technologies, and comprehensively utilizes internationally accredited latest such as Cryosurgical Ablation (CSA), Cancer Vascular Intervention Therapy (CVI), and combined immunotherapy (CIC). Give from local to whole body treatment according to different situation. It is a better choice for patients with tumors that are unresectable, metastatic, recurrent or/and unresponsive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy. More details>>
Cryosurgical Ablation (CSA)
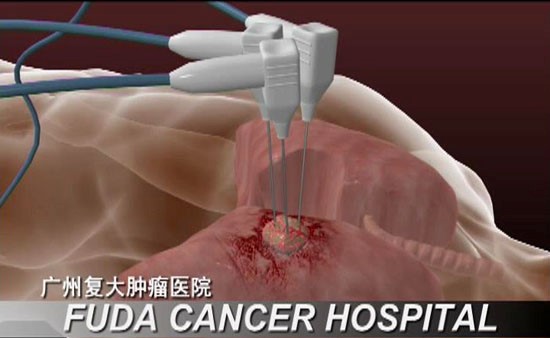
Unlike other ablation methods, cryotherapy not only ablates tumor tissue in situ, but also stimulates systemic anti-tumor immunity to eliminate residual or metastatic lesion, thereby reducing or preventing recurrence.
Cryosurgical ablation can prolong survival time of patients with liver cancer. Zhou Xinda et al [2] reported that survival rates of 1 year, 3 years and 5 years in 235 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who have received intraopertive cryosurgery are 78.4%, 54.1% and 39.8% respectively, which is higher than that of patients who underwent surgical resection alone. The survival rate of primary or secondary liver cancer patients treated mainly with percutaneous cryotherapy is much higher than that of patients who received general chemotherapy [3-6].
Irreversible Electroporation (IRE)
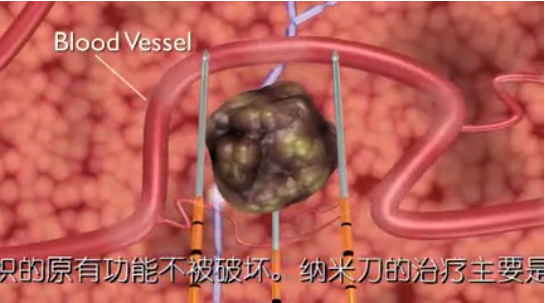
NanoKnife ablation can more precisely induce apoptosis of tumor cells and cause complete ablation of tumors without irreversible damage to other important tissues in the ablation area, such as blood vessels, bile ducts, nerves, etc., thereby reducing the complications associated with other traditional methods of ablation.
Cancer Vascular Intervention (CVI)
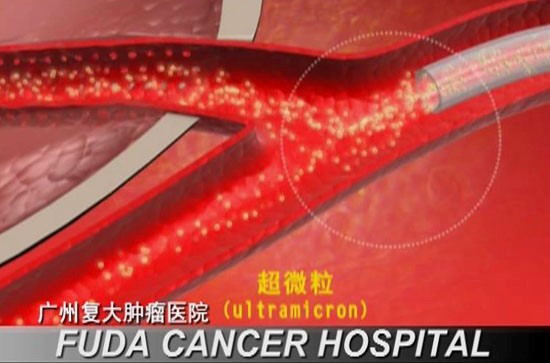
Drug microspheres will be injected into the tumor, and the microspheres will selectively penetrate into the tumor tissue and maintain a high concentration for a long time. The chemotherapeutic drugs that reach the normal capillaries are too small to cause capillary embolism and flow along with the blood flow. In addition, the dosage of the chemotherapeutic drugs is very low, so it will not cause too much damage to the normal tissues. Systemic side effects are very small [7].
Combined Immunotherapy (CIC)

A variety of immunotherapies are combined together to eliminate cancer cells and leave the remaining cancer cells in a dormant state, allowing patients to survive for a long time without any side effects.