Recently, Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital successfully performed the world's first clinical trial of malignant pulmonary nodule ablation using the "Wknife" technique under local anesthesia. The surgery was led by President Niu Lizhi.

The patient undergoing this treatment is a 59-year-old male diagnosed with postoperative recurrence of retroperitoneal metastatic adenocarcinoma and secondary malignant tumors in both lungs. Systemic medical treatment, radiotherapy, and cryoablation of local lung metastases were performed, and the lesions in the original ablation area were well controlled. Consider the left lower pulmonary nodule advanced, and repeated cryoablation has a greater impact on lung function. Therefore, after consultation with the hospital's MDT, it was decided to use the "Wknife" technique for minimally invasive ablation therapy.
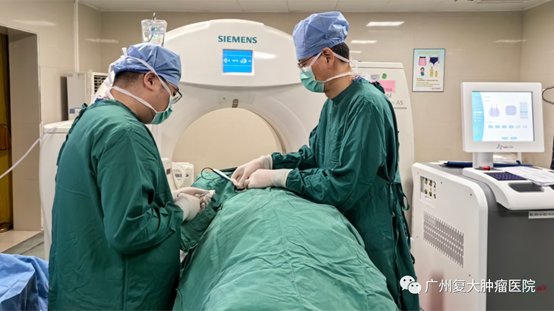
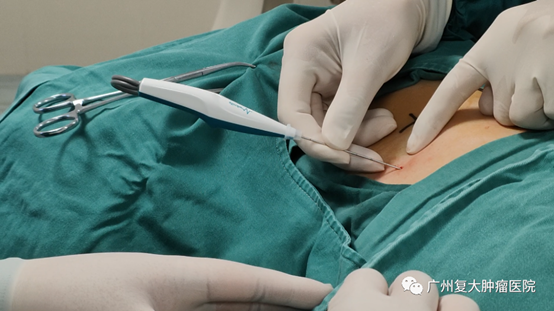
During the entire surgical procedure, the patient received local anesthesia and the "Wknife" was used under CT guidance to perform the targeted ablation on the lesion area using single probe; No muscle relaxants or tracheal anesthesia were used during the operation. The patient was awake during the procedure, with no visible muscle contractions and no obvious pain or discomfort; Immediately after the surgery, CT showed that the ablation effect met expectations. The patient's vital signs were stable during and after the surgery, and no adverse reactions were observed.
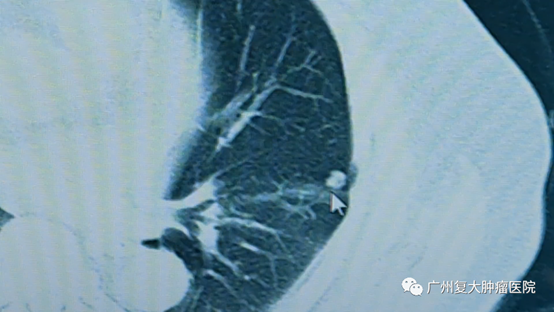
Before operation
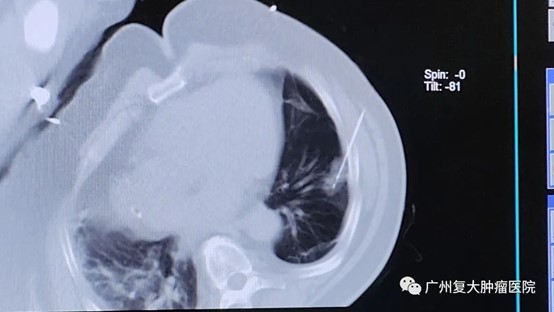
during operation
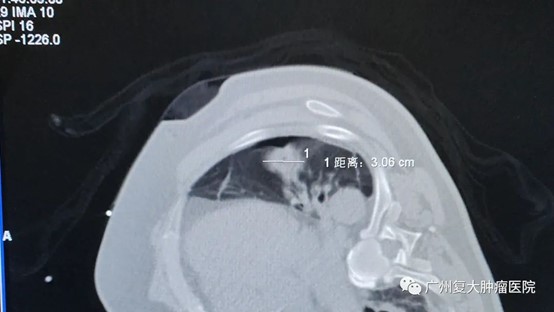
after operation
Pulmonary nodules refer to nodular shadows within the lung parenchyma that are not part of normal lung tissue. The size generally does not exceed 3 cm. If it exceeds 3 cm, it is called a lung tumor. Pulmonary nodules can be divided into benign and malignant. Benign pulmonary nodules generally do not require treatment and only require regular check-up. However, Malignant pulmonary nodules require timely treatment to prevent the spread of cancer cells. There are many treatments for suspected malignant pulmonary nodules, two of the more common ones are surgery and ablation.
The "Wknife" technology works on the principle of irreversible cell electroporation induced by pulsed electric fields, leading to the destruction of tumor tissue. It is a non-thermal, selective physical ablation technique that can achieve tumor ablation while preserving the integrity of important ductal structures (blood vessels, bile ducts, and nerves) around the tumor, without any thermal effects or perivascular tumor cells remained.
This technology is the latest generation of IRE technology, integrating the advantages of the previous two generations, namely the microsecond pulse electric perforation technology (traditional IRE) and the high-frequency pulse electric field ablation technology (HF-IRE). This technology can solve the problems of high anesthesia requirements, strong muscle contractions, difficult needle insertion, and limited ablation area in the existing IRE technology, making IRE tumor ablation therapy more efficient, safe and convenient for patients, and is expected to become a new option for malignant pulmonary nodules treatment.
As a National Key Clinical (Oncology) hospital, Guangzhou Fuda Cancer Hospital is under the management of the Guangdong Provincial Health Commission. It is a modern, international cancer hospital that integrates medical treatment, teaching, scientific research and preventive health care, embracing high and new technologies. The used of "Wknife" and the newly developed single-probe ablation technic have achieved the leap from "general anesthesia" to "local anesthesia" in IRE technology, reducing the difficulty of surgical operations and benefiting patients. This is an innovation in clinical practice, marking that Fuda has reached a new level in the field of minimally invasive tumor ablation.